Utility of Anthropometric tools in determining Obesity in children
Main Article Content
Abstract
Measurement of excess body fat objectively requires the use of investigations like Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance imaging, which are generally not easily accessible, expensive and may involve exposure to radiation. Use of anthropometric measures have been used with various levels of sensitivity. We therefore set out to determine the predictive ability of Body mass index(BMI) and waist to height ratio(WHtR) in determining Obesity in children.
Methods: Students in classes 4 and 5 from four different primary schools in North central Nigeria were recruited after ethical clearance was obtained from the Ethical review board of the State. Height, Weight, Waist circumference (WC) were measured. Percentage body fat was measured using a Tanita (BC-543 model) bioimpedance scale. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS version 20.
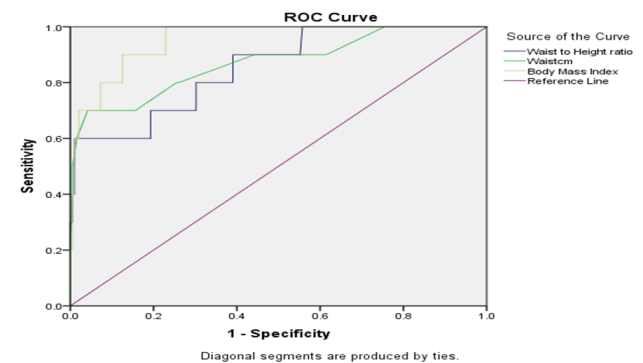
Results: A total of 202 pupils from 4 randomly selected primary schools (2 private and 2 public schools) within the Ilorin metropolis were recruited for the study consisting of 90 males and 112 females. Prevalence of obesity and central obesity using body fat from bioimpedance and WHtR were 4.95% and 11.4% respectively. Both BMI and WHtR correlated well with Percentage body fat in determining Obesity. The area under curve was 0.853 for WHtR, 0.871 for WC and 0.930 for BMI (P value for all: 0.000)
Conclusion: WHtR, WC and BMI are very good tools for determining Obesity in children and can be used as surrogates for determining excess body fat.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
How to Cite
References
World Health Organization. Newsroom. 2021 [cited 2023 May 27]. Obesity and overweight. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
Kahn HS, Bullard KM, Barker LE, Imperatore G. Differences between adiposity indicators for predicting all-cause mortality in a representative sample of United States non-elderly adults. PLoS One [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2019 Apr 3];7(11):e50428. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23226283
Navaneethan SD, Kirwan JP, Remer EM, Schneider E, Addeman B, Arrigain S, et al. Adiposity, Physical Function, and Their Associations With Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Adipokines in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis [Internet]. 2021 Jan 1 [cited 2021 Apr 8];77(1):44–55. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32798563/
Sweeting HN. Measurement and definitions of obesity in childhood and adolescence: A field guide for the uninitiated. Nutr J [Internet]. 2007 Oct 26 [cited 2024 May 7];6(1):1–8. Available from: https://link.springer.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2891-6-32
Van Haute M, Rondilla E, Vitug JL, Batin KD, Abrugar RE, Quitoriano F, et al. Assessment of a proposed BMI formula in predicting body fat percentage among Filipino young adults. Sci Reports 2020 101 [Internet]. 2020 Dec 15 [cited 2024 Apr 27];10(1):1–14. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-79041-3
Wang L, Hui SSC. Validity of Four Commercial Bioelectrical Impedance Scales in Measuring Body Fat among Chinese Children and Adolescents. Biomed Res Int [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2024 Apr 27];2015. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC4475745/
Aristizabal JC, Barona-Acevedo J, Estrada-Restrepo A. Correlation of body mass index and waist to height ratio with cardiovascular risk factors in Colombian preschool and school children. Colomb Médica C [Internet]. 2023 May 16 [cited 2024 May 7];54(1). Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC10324468/
Huxley R, Mendis S, Zheleznyakov E, Reddy S, Chan J. Body mass index, waist circumference and waist:hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular riska review of the literature [Internet]. Vol. 64, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Nature Publishing Group; 2010 [cited 2020 Sep 11]. p. 16–22. Available from: www.nature.com/ejcn
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Identifying and assessing overweight, obesity and central adiposity | Overweight and obesity management | Guidance | NICE [Internet]. NICE; 2025 [cited 2025 Jan 15]. Available from: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng246
De Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A, Nishida C, Siekmann J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ [Internet]. 2007 Sep [cited 2024 Oct 21];85(9):660. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2636412/
Ogden CL, Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM, Mei Z, Guo S, Wei R, et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2000 growth charts for the United States: Improvements to the 1977 National Center for Health Statistics version. Pediatrics. 2002;109(1):45–60.
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ [Internet]. 2000 May 6 [cited 2024 Oct 21];320(7244):1240–3. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10797032/
Moselakgomo VK, van Staden M. Diagnostic comparison of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and International Obesity Task Force criteria for obesity classification in South African children. African J Prim Heal care Fam Med [Internet]. 2017 Aug 31 [cited 2024 Oct 21];9(1). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28893079/
Adom T, Kengne AP, Villiers A De, Boatin R, Puoane T. Diagnostic Accuracy of Body Mass Index in Defining Childhood Obesity: Analysis of Cross-Sectional Data from Ghanaian Children. Int J Environ Res Public Health [Internet]. 2019 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Oct 21];17(1):36. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6981394/
Llorca-Colomer F, Murillo-Llorente MT, Palau-Ferré A, Pérez-Bermejo M, Legidos-García ME. Differences in Classification Standards For the Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Epidemiol [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2024 Oct 21];14:1031. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9444235/
Desalew A, Mandesh A, Semahegn A. Childhood overweight, obesity and associated factors among primary school children in dire dawa, eastern Ethiopia; a cross-sectional study. BMC Obes [Internet]. 2017 Jun 1 [cited 2020 Nov 17];4(1):1–10. Available from: https://link.springer.com/articles/10.1186/s40608-017-0156-2
Costa-Urrutia P, Vizuet-Gámez A, Ramirez-Alcántara M, Guillen-González MÁ, Medina-Contreras O, Valdes-Moreno M, et al. Obesity measured as percent body fat, relationship with body mass index, and percentile curves for Mexican pediatric population. PLoS One. 2019;14(2).
Di Cesare M, Sorić M, Bovet P, Miranda JJ, Bhutta Z, Stevens GA, et al. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: a worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med [Internet]. 2019 Nov 25 [cited 2024 May 9];17(1). Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC6876113/
Ashwell M. Charts based on body mass index and waist-to-height ratio to assess the health risks of obesity: A review. Open Obes J. 2011;3:78–84.
Santomauro F, Lorini C, Pieralli F, Niccolai G, Picciolli P, Vezzosi S, et al. Waist-to-height ratio and its associations with body mass index in a sample of Tuscan children in primary school. Ital J Pediatr [Internet]. 2017 Jun 7 [cited 2023 May 15];43(1):1–6. Available from: https://ijponline.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13052-017-0372-x
Browning LM, Hsieh SD, Ashwell M. A systematic review of waist-to-height ratio as a screening tool for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: 0·5 could be a suitable global boundary value. Nutr Res Rev [Internet]. 2010 Dec [cited 2024 May 8];23(2):247–69. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20819243/
Park SH, Choi SJ, Lee KS, Park HY. Waist Circumference and Waist-to-Height Ratio as Predictors of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Adults. Circ J [Internet]. 2009 Sep [cited 2020 Sep 11];73(9):1643–50. Available from: http://joi.jlc.jst.go.jp/JST.JSTAGE/circj/CJ-09-0161?from=CrossRef
Özhan B, Ersoy B, Özkol M, Kiremitci S, Ergin A. Waist to height ratio: a simple screening tool for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. Turk J Pediatr [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2024 May 7];58(5):518–23. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28621093/
Valle-Leal J, Abundis-Castro L, Hernández-Escareño J, Flores-Rubio S. [Waist-to-height ratio is an indicator of metabolic risk in children]. Rev Chil Pediatr [Internet]. 2016 May 1 [cited 2024 May 7];87(3):180–5. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26701618/
Aguilar-Morales I, Colin-Ramirez E, Rivera-Mancía S, Vallejo M, Vázquez-Antona C. Performance of waist-to-height ratio, waist circumference, and body mass index in discriminating cardio-metabolic risk factors in a sample of school-aged Mexican children. Nutrients. 2018 Dec 1;10(12).
Blüher S, Molz E, Wiegand S, Otto KP, Sergeyev E, Tuschy S, et al. Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, and Waist-to-Height Ratio as Predictors of Cardiometabolic Risk in Childhood Obesity Depending on Pubertal Development. J Clin Endocrinol Metab [Internet]. 2013 Aug 1 [cited 2023 May 17];98(8):3384–93. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/98/8/3384/2834196
Martin-Calvo N, Moreno-Galarraga L, Martinez-Gonzalez MA. Association between Body Mass Index, Waist-to-Height Ratio and Adiposity in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients [Internet]. 2016 Aug 20 [cited 2024 May 8];8(8). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27556485/
Bener A, Yousafzai MT, Darwish S, Al-Hamaq AOAA, Nasralla EA, Abdul-Ghani M. Obesity index that better predicts metabolic syndrome: Body mass index, waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, or waist-height ratio. J Obes. 2013;2013.
Mushtaq MU, Gull S, Abdullah HM, Shahid U, Shad MA, Akram J. Waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, and waist-height ratio percentiles and central obesity among Pakistani children aged five to twelve years. BMC Pediatr. 2011 Nov 21;11.
Day K, Kwok A, Evans A, Mata F, Verdejo-Garcia A, Hart K, et al. Comparison of a Bioelectrical Impedance Device against the Reference Method Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Anthropometry for the Evaluation of Body Composition in Adults. Nutr 2018, Vol 10, Page 1469 [Internet]. 2018 Oct 10 [cited 2024 May 9];10(10):1469. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/10/10/1469/htm