Psycho-Social Characteristics of Patients with Substance Use Disorder Seen at the Sierra Leone Psychiatric Teaching Hospital (USLTHC), Freetown, Sierra Leone
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background
The rising incidence of substance use in Sierra Leone poses a public health concern. Its impact on the country and her citizenry particularly the youths has multifaceted negative implications. This study sought to examine the psychosocial characteristics of patients with substance abuse disorder seen at the Sierra Leone Psychiatric Teaching Hospital, Kissy.
Methods
The study employed a cross-sectional design. One hundred and sixty-five respondents being treated for substance use disorder were consecutively recruited between October, 2023 and April, 2024. Data was drawn from a “Reflection Form” designed by one of the authors (CEO) to elicit information in the course of psychotherapy with patients. SPSS version 29 was used to analyse the data.
Results
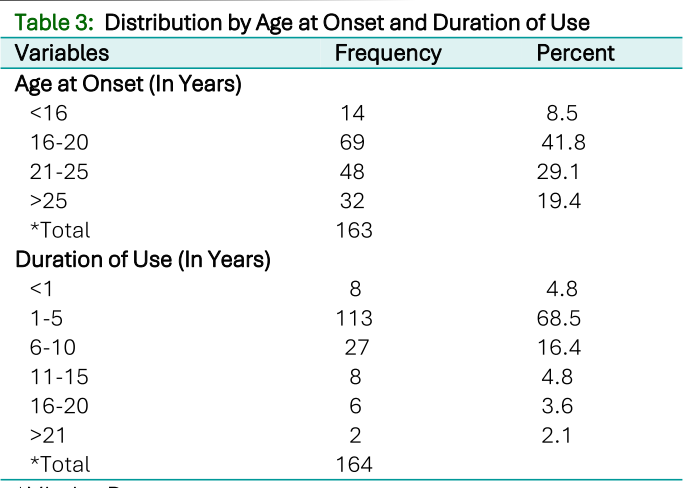
More males (79.4%) were found to use psychoactive substances. The majority of the substance users were students (60.6%). Kush was found to be the most used psychoactive substance (76.4%). A desire for improved sleep, increased appetite, facilitation of meditation, peer group influence (76.4%) and stress (73.3%) were reasons given for taking psychoactive substances. The source of funding substance use was stealing (32.1%), sale of property (17.0%), begging (15.2%), allowance (46.7%) and earnings (58.2%). The age range at onset for most of the respondents was between 16 and 25 years. A majority of the respondents (68.5%) have used psychoactive substances for a duration of 1 to 5 years.
Conclusion
The predominant involvement of students in substance use found in this study calls for public and school-based enlightenment campaigns. In view of the manifold implications of early onset of substance use, stringent policies, sanctions, community intervention and family involvement should be upheld to curtail substance abuse in young persons.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
How to Cite
References
Kaldor, Mary; Vincent, James (2006). Evaluation of UNDP assistance to conflict-affected countries: Case Study: Sierra Leone (PDF). New York City: United Nations Development Programme. p. 4. Retrieved 28 August 2021.
Jalloh M. F., Li W., Bunnell R. E., et al (2018) Impact of Ebola experiences and risk perceptions on mental health in Sierra Leone, July 2015. BMJ Global Health, 3, e000471.
Sierra Leone declares drug abuse “national emergency” dw/com/enco-68728880
United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) (2018) Sierra Leone 2015 Population and Housing Census National Analytical Report. UNFPA.
Olawole-Isaac A, Ogundupe O, Davies A. Substance use among adolescents in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. South Afr J Child Health. (2018) 12:79. doi: 10.7196/SAJCH.2018.v12i2b.1524
Simon KM, Levy SJ, Bukstein OG. (2022). Adolescent substance use disorders. NEJM Evid. 1: EVIDra2200051. doi: 10.1056/EVIDra2200051
GBD. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1789–858. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32279-7
Morojele NK, Ramsoomar L, Dumbili EW, Kapiga S. (2021) Adolescent Health Series – Alcohol, tobacco, and other drug use among adolescents in sub-Saharan Africa: A narrative review. Trop Med Int Health. 26:1528–38. doi: 10.1111/tmi.13687
Leikin JB. Substance-related disorders in adults. Dis Mon 2007; 53: 313-335 [PMID: 17645897 DOI: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2007.04.001]
Ebrahim J, Adams J and Demant D (2024) Substance use among young people in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 15:1328318. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1328318
Mutepfa M. (2021). Substance Use and Misuse in sub-Saharan Africa Trends, Intervention, and Policy: Trends, Intervention, and Policy. Cham, Switzerland: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-85732-5.
Ritchwood TD, Ford H, DeCoster J, Sutton M, Lochman JE. (2015). Risky sexual behavior and substance use among adolescents: A meta-analysis. Child Youths Serv Rev. 52:74–88. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouths.2015.03.005
Oppong Asante K, Meyer-Weitz A, Petersen I. (2014) Substance use and risky sexual behaviours among street connected children and youths in Accra, Ghana. Subst Abuse Treat Prevent Policy. 9:45. doi: 10.1186/1747-597X-9-45
Jere DL, Norr KF, Bell CC, Corte C, Dancy BL, Kaponda CPN, et al. (2017). Substance Use and Risky Sexual Behaviors Among Young Men Working at a Rural Roadside Market in Malawi. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 28:280–90. https://journals.lww.com/janac/ fulltext/2017/03000/substance_use_and_risky_sexual_behaviors_among.7.aspx.
McLellan AT. Substance Misuse and Substance use Disorders: Why do they Matter in Healthcare? Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. (2017) 128:112–30.
Sanchez-Roige S, Kember RL, Agrawal A. Substance use and common contributors to morbidity: A genetics perspective. eBioMedicine. (2022) 83:104212. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104212
Daley DC. (2013) Family and social aspects of substance use disorders and treatment. J Food Drug Anal. 21:S73–s76. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2013.09.038
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2021. [cited 15 January 2022]. Available from: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/data-and-analysis/wdr2021.html
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2021. [cited 15 January 2022]. Available from: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/data-and-analysis/wdr2021.html
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2019. [cited 15 January 2022]. Available from: https://wdr.unodc.org/wdr2019/
Onalapo, O.J, Olofinnade, A.T, Ojo, F.O, Adeleye, O. Falade, J. & Onolapo, A.Y Substance use and substance use disorders in Africa: An epidemiological approach to the review of existing literature. World J Psychiatry 2022 October 19; 12(10): 1268-1286
Akyeampong E. K., Hill A. G. & Kleinman A (editors). (2015) The Culture of Mental Illness and Psychiatric Practice in Africa: 349. Indiana University Press.
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Drug use in Nigeria. [cited 15 January 2022].Availablefromhttps://www.unodc.org/documents/dataanalysis/statistics/Drugs/Drug_Use_Survey_Nigeria_2019_BOOK.pdf
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Drug Report 2016. [cited 15 January 2022]. Available from: https://www.unodc.org/wdr2016/
Oshodi O, Aina O, Onajole A. Substance use among secondary school students in an urban setting in Nigeria: prevalence and associated factors. African J Psychiatry. 2010;13(1):52–7. 10.4314/ajpsy. v13i1.53430. [PubMed]
Mahanta B, Mohapatra PK, Phukan N, Mahanta J: Alcohol use among school-going adolescent boys and girls in an industrial town of Assam, India. Indian J Psychiatry. 2016, 58:157-63. 10.4103/0019-5545.183784
Sivapuram MS, Nagarathna R, Anand A, Patil S, Singh A, Nagendra HR: Prevalence of alcohol and tobacco use in India and implications for COVID-19 - Niyantrita Madhumeha Bharata Study Projections. J Med Life. 2020, 13:499-509. 10.25122/jml-2020-0079.
Kyei-Gyamfi S, Kyei-Arthur F, Alhassan N, Agyekum MW, Abrah PB, Kugbey N. Prevalence, correlates, and reasons for substance use among adolescents aged 10–17 in Ghana: a cross-sectional convergent parallel mixed-method study. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2024 Feb 29; 19(1):17. https:// doi.org/10.1186/s13011-024-00600-2 PMID: 38424633
Jatau AI, Sha'aban A, Gulma KA, Shitu Z, Khalid GM, Isa A, Wada AS, Mustapha M. The Burden of Drug Abuse in Nigeria: A Scoping Review of Epidemiological Studies and Drug Laws. Public Health Rev 2021; 42: 1603960 [PMID: 33796340 DOI: 10.3389/phrs.2021.1603960]
Teferra S. Substance use among university students in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ethiop J Health Dev 2018; 32: 265-277
UNODC. UNODC Early Warning Advisory on New Psychoactive substances. [cited 15 January 2022]. Available from: https://www.unodc.org/LSS/Home/NPS
Peacock A, Bruno R, Gisev N, Degenhardt L, Hall W, Sedefov R, White J, Thomas KV, Farrell M, Griffiths P. New psychoactive substances: challenges for drug surveillance, control, and public health responses. Lancet 2019; 394: 1668- 1684 [PMID: 31668410 DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32231-7
Klein A. Drug Problem or Medicrime? Distribution and Use of Falsified Tramadol Medication in Egypt and West Africa. J Illicit Econ Dev. 2019; 1:52–62.
Akande S. A new deadly form of marijuana is slowly wreaking havoc in Nigeria’s cities. Jul 24, 2017. [cited 15 January 2022]. Available from:https://www.pulse.ng/gist/synthetic-marijuana-black-mamba-a-new-deadly-formofmarijuanaisslowlywreaking/r4dmxpn#:~:text=A%20new%20deadly%20form%20of%20marijuana%20is%20slowly,that%20can%20lead%2 0to%20death.%20%7C%20Pulse%20Nigeria
Trenchard, T. Cheap, plentiful and devasting: A synthetic drug Kush is walloping Sierra Leone (2024) https://www.npr.org
Nath A, Choudhari S G, Dakhode S U, et al. (November 07, 2022) Substance Abuse Amongst Adolescents: An Issue of Public Health Significance. Cureus 14(11): e31193. DOI 10.7759/cureus.31193
Abu, R. et al (2024) Beyond the Smoke: A Phenomenological Study of Health and Social Implications of Kush Use Among Sierra Leonean Youthss Ronald Abu Bangura1&, Alhassan Mayei1&, doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.24.243060831
Ofovwe, CE (2011) Fundamentals of General and Clinical Psychology Mindex Publishing co. Ltd. Benin City, Nigeria
Koob, G. F. (2013) The role of stress in addiction. Clinical Psychological Science, 1(2), 141-155
Merikangas KR, McClair VL. Epidemiology of substance use disorders. Hum Genet 2012; 131: 779-789 [PMID: 22543841 DOI: 10.1007/s00439-012-1168-0]
Macleod J, Oakes R, Copello A, Crome I, Egger M, Hickman M, Oppenkowski T, Stokes-Lampard H, Smith GD. Psychological and social sequelae of cannabis and other illicit drug use by young people: a systematic review of longitudinal, general population studies. The Lancet. 2004;363(9421):1579–88.